
1. Find out my partner.
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| 1. Heartbeats | a. 350 ml |
| 2. RBC | b. 7.4 |
| 3. WBC | c. 37° C |
| 4. Blood donation | d. 72 per min |
| 5. Normal body temperature | e. 50 – 60 lakh/mm3 |
| 6. pH of oxygenated blood | f. 5000 – 6000 per mm3 |
Answer:
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| 1. Heartbeats | d. 72 per min |
| 2. RBC | e. 50 – 60 lakh/mm3 |
| 3. WBC | f. 5000 – 6000 per mm3 |
| 4. Blood donation | a. 350 ml |
| 5. Normal body temperature | c. 37° C |
| 6. pH of oxygenated blood | b. 7.4 |
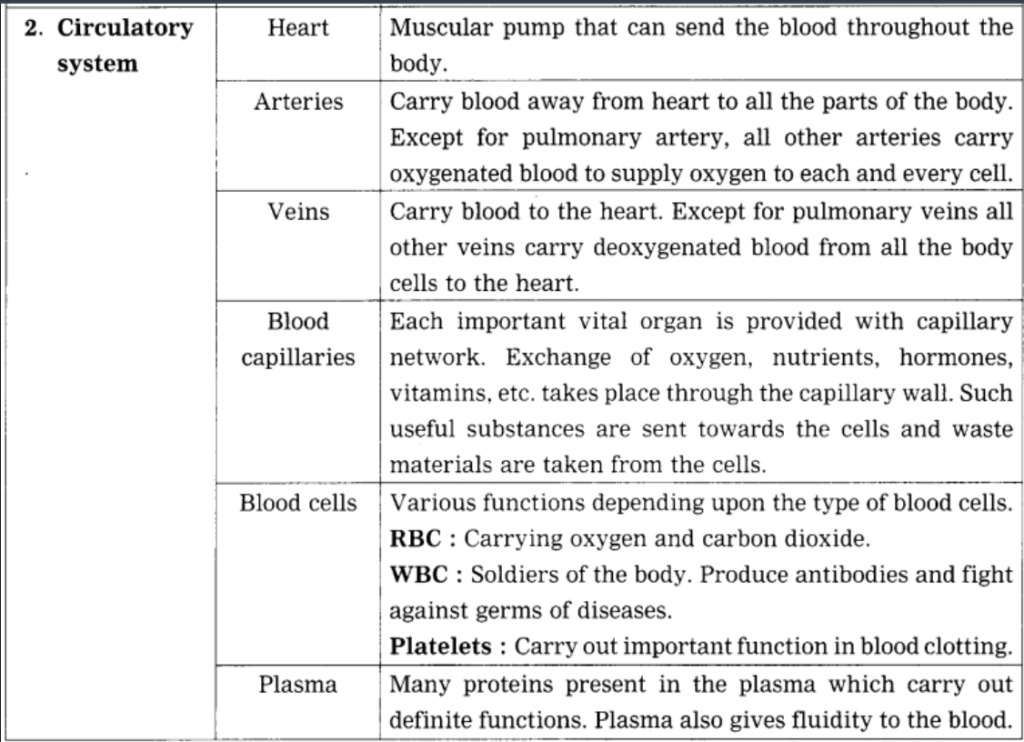
2. Complete the following table.
Question a.
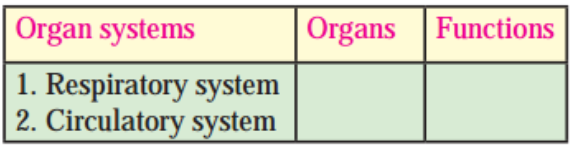
Answer:

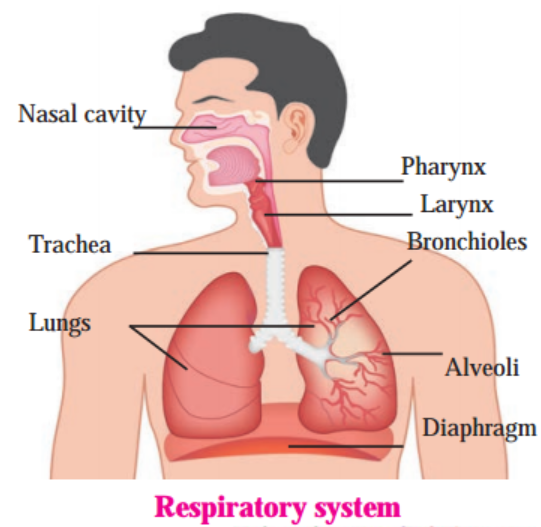
3. Draw neat and labeled diagrams.
a. Respiratory system.
Answer:
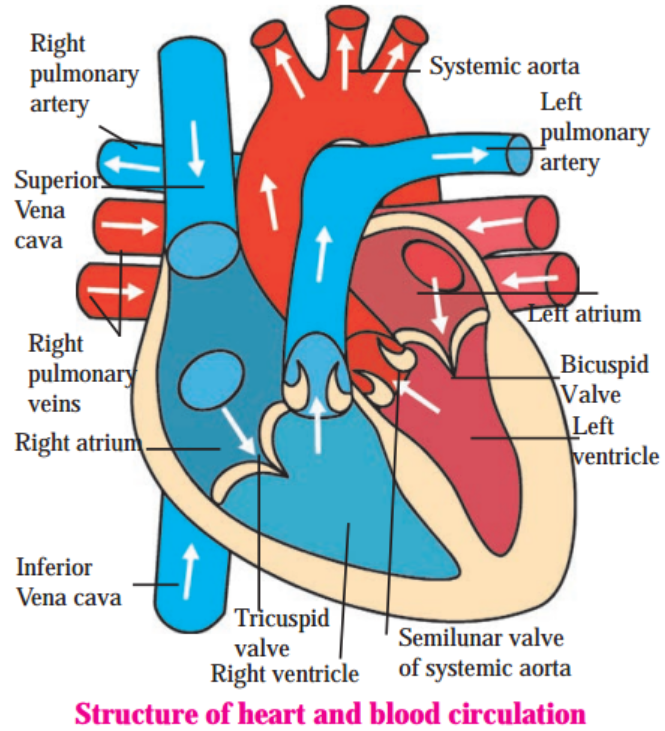
b. Internal structure of heart.
Answer:

4. Explain with reasons.
a. Human blood is red coloured.
Answer:
The red colour of human blood is due to hemoglobin which is a red coloured conjugated protein with iron that is present on the red blood cells. Therefore, it looks red.
b. Upward and downward movement of diaphragm occurs consecutively.
Answer:
The breathing movements are possible due to contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm. The rib muscles also help in these movements. When the ribs rise and diaphragm is lowered at the same time, then there is a decrease in pressure on lungs.
This causes movement of air into the lungs at the time of inhalation. On the other hand, when ribs come back to their normal position and diaphragm is risen, then pressure on the lungs increases. This causes movement of the air out of the body through the nose in the form of exhalation. These movements are possible only due to consecutive upward and downward movement of the diaphragm.
c. Blood donation is considered to be superior of all donations.
Answer:
Blood cannot be manufactured by any artificial chemical process. The only way to obtain blood is by donations of blood from a live donor. Blood is needed at times of emergency. The life of person can be saved if timely blood transfusion is given to the needy victim or a patient. Since such donation can save a valuable human life, it is called superior of all donations.
d. Person with ‘O’ blood group is considered as ‘universal donor’.
Answer:
Person with ‘O’ blood group does not have any antigen on his/her RBCs. The ‘O’ type blood thus cannot cause clotting reactions in the body of the recipients. Such persons with ‘O’ blood group can donate blood to any person having any blood group therefore they are considered as ‘universal donor’.
e. Food must have limited amount of salts.
Answer:
More salt in diet means more sodium ions. These extra sodium salts cause rise in blood pressure. Such condition is called hypertension. This condition can be dangerous and fatal in some cases. Therefore, one must keep control over sodium content of the food.
5. Answer the following questions in your own words.
a. Explain the functional correlation of circulatory system with respiratory, digestive and excretory system.
Answer:
1. Three systems viz. respiratory, digestive and circulatory always work in coordination.
2. Digestive system helps in breaking down complex food molecules into simple soluble nutrients at the end of the digestion process.
3. The soluble nutrients are absorbed in the circulating blood in the villi of the intestine.
4. The blood carries these nutrients to each cell during its circulation.
5. The respiratory system helps the oxygen from the air to be absorbed in the blood.
6. This process takes place in alveolus present in lungs. The oxygen is absorbed in the blood and through haemoglobin it is taken to every cell of the body. At the same time the unwanted carbon dioxide produced in each cell is given out in a process of gaseous exchange.
7. The soluble nutrients, and chiefly glucose is metabolized with the help of oxygen-producing energy. Thus, all the three systems bring about coordinated functions to keep the body alive.
b. Explain the structure and function of human blood.
Answer:
I. Structure, i.e. components of the human blood: Human blood is a fluid connective tissue consisting of blood plasma and blood corpuscles suspended in it.
1. Plasma: Plasma is the fluid part of the blood which is pale yellow in colour. It is slightly alkaline in nature. It has 90-92% water, 6-8 % proteins and 1-2 % inorganic salts.
It contains proteins such as albumin, globulin, fibrinogen, etc. There are inorganic ions such as Ca, Na and K.
2. Blood cells:
a. Blood cells are mainly of three types, viz. RBCs, WBCs and blood platelets. They are produced in the red bone marrow.
b. RBCs are small, circular and enucleated cells. They are full of haemoglobin which is essential in transporting oxygen. RBCs are red blood cells which are 50 to 60 lakh per cubic millimetre. Their life span is 100 to 127 days.
c. WBCs are large, nucleated and colourless. They are of five subtypes, viz. neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, monocytes and lymphocytes. They are 5 to 10 thousands per millimetre of blood.
d. Platelets are very small disc-shaped blood cells which are 2.5 to 4 lakh per cubic millimetre of blood.
II. Function of human blood:
1. Transport functions:
- Gases: Oxygen is carried via blood from lungs to cells in various parts of body and carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs.
- Nutrients: Simple nutrients like glucose, amino acids, fatty acids are taken up by blood from wall of alimentary canal and transported up to each cell in the body.
- Waste materials: Nitrogenous wastes like ammonia, urea, creatinine are released by tissues into blood which carries those to kidney for excretion.
- Enzymes and hormones: Blood transports the enzymes and hormones from the site of their production to the site of their action.
2. Protection: Antibodies are produced in the blood and they protect the body from microbes and other harmful particles.
3. Thermoregulation: Body temperature is maintained constant at 37 °C by vasodilation and vasoconstriction.
4. Maintaining the balance of minerals like Na, K in the body.
5. If bleeding occurs at the injury, platelets and a protein called fibrinogen of the blood form a clot and seal the injury.
6. Functions of blood cells:
- RBCs: With haemoglobin it carries out transport of respiratory gases.
- WBCs: Soldiers of the body. Produce antibodies and give immunity to body.
- Platelets: Help in blood clotting.
c. Explain the importance and need of blood donation.
Answer:
Blood can never be synthesized artificially. There is no substitute for natural blood. Every healthy person possesses about 5 litres of blood in his or her body. In case of haemorrhage i.e. blood loss, the blood volume may reduce which can result into threat to life. Moreover, the loss of blood should be immediately taken care of, otherwise it may cost the life.
Therefore blood transfusion is very crucial in case of victims of accidents, patients of surgeries or mothers who suffer from blood loss during childbirth (parturition). Some diseases such as thalassemia, blood cancer, etc. also need regular transfusions. Therefore, blood is always needed in many such conditions. Blood donation is only option for such transfusions.
6. Explain the differences.
a. Arteries and veins.
Answer:
| Arteries | Veins |
| 1. Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the tissues of the body. | 1. Veins carry blood from the tissues of the body back to the heart. |
| 2. Arteries are located deeper within the body. | 2. Veins are usually located superficially beneath the surface of the skin. |
| 3. Arteries are thick walled | Veins are thin walled. |
| 4. Arteries do not have valves. | 4. Veins have valves. |
| 5. Arteries would generally remain open if blood flow stopped, due to their thick muscular layer. | 5. Veins would collapse if blood flow stops. |
| 6. Except pulmonary artery, all arteries carry oxygenated blood. | 6. Except pulmonary vein, all veins carry deoxygenated blood. |
| 7. Arteries are more muscular than veins, which helps in transporting blood that is full of oxygen efficiently to the tissues. | 7. Veins are less muscular than arteries, but contain valves to help keep blood flowing in the right direction, usually toward the heart. |
| 8. There is maximum blood pressure in the arteries. | 8. There is minimum blood pressure in the veins. |
b. External and internal respiration.
Answer:
| External respiration | Internal respiration |
| 1. Intake of air from the outside into the body and release of air from the body to outside is called external respiration. | 1. Exchange of gases between cells and tissue fluid is called internal respiration. |
| 2. External respiration occurs between cells and the external environment. | 2. Internal respiration occurs only in the cells of the body. |
| 3. It involves processes of inspiration and expiration. | 3. It involves movement of O2 from blood into tissue fluid and movement of CO2 from tissue. |
| 4. External respiration involves breathing and gaseous exchange. | 4. Internal respiration involves neither breathing nor gaseous exchange. |
| 5. Oxygen combines with haemoglobin in external respiration. | 5. Chemical reactions occur in the cells to form energy. |
7. Which health parameters of blood donor should be checked?
Answer:
Blood donor should be healthy. He or she should have good haemoglobin’s content. The RBC and WBC count should also be normal. They should not carry any parasites in their blood such as malarial parasite or dengue virus. The donor should not be HIV positive or should not have any infectious diseases. He should not have any addictions such s drug-abuse or alcohol consumption.
8. Fill in the blanks using appropriate words given in the bracket.
(hemoglobin, alkaline, diaphragm, red bone marrow, acidic, voluntary, involuntary,)
Question a.
RBCs of the blood contain ……….., an iron compound.
Answer:
RBCs of the blood contain haemoglobin, an iron compound.
Question b.
……………….. is present between thoracic and abdominal cavity.
Answer:
Diaphragm is present between thoracic and abdominal cavity.
Question c.
Cardiac muscles are …………… .
Answer:
Cardiac muscles are involuntary.
Question d.
pH of oxygenated blood is …………… .
Answer:
pH of oxygenated blood is alkaline.
Question e.
Production of RBCs occurs in ……………… .
Answer:
Production of RBCs occurs in red bone marrow.
9. Find odd one out.
Question a.
A, O, K, AB, B.
Answer:
K (All others are blood groups.)
Question b.
Blood plasma, platelets, blood transfusion, blood corpuscles.
Answer:
Blood transfusion (All others are components of blood.)
Question c.
Trachea, alveoli, diaphragm, capillaries.
Answer:
Capillaries (All others are parts of respiratory system. Capillaries exist throughout the body.)
Question d.
Neutrophils, globulins, albumins, prothrombin.
Answer:
Neutrophils (All others are proteins present in the plasma.)
10. Read the following paragraph and identify the disease.
Today, her child became one and half year old. However, that child does not seem to be healthy and happy. It was continuously crying and gradually becoming weak. It has shortness of breath. Its nails have become blue.
Answer:
The heart of the child is not functioning properly. Bluish nails show lack of oxygen, thus the baby may be suffering also from respiratory problems.
11. Your neighboring uncle has been diagnosed with hypertension. What should he do to keep his blood pressure within normal range?
Answer:
Hypertension has many causes. Try to find out what is the exact cause. Is it lack of exercise, obesity, lots of fast and junk food consumption, over-intake of salt, mental tension, etc. He should visit a proper physician and take prescribed blood pressure control medicines. He should never miss a single tablet. He should avoid salty and preserved food. He should practice yoga and meditation. He should also undertake some stress- management techniques.


