1. Fill ¡n the blanks with the proper words from the brackets.
(stationary, zero, changing, constant, displacement, velocity, speed. acceleration, stationary but not zero. inc reuses)
a. If a body traverses a distance in direct proportion to the time, the speed of the body is ……………… .
Answer:
constant
b. If a body is moving with a constant velocity, its acceleration is ……………… .
Answer:
zero
c. ……………. is a scalar quantity.
Answer:
Speed
d. …………….. is the distance traversed by a body in a particular direction in unit time.
Answer:
Velocity
2. Observe the figure and answer the questions.
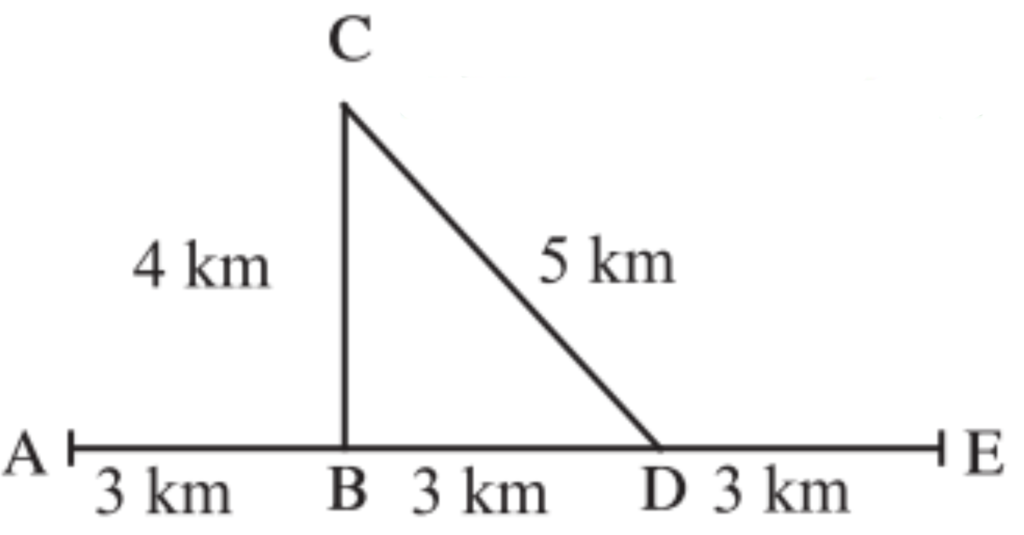
Sachin and Sarneer started on a motorbike from place A, took the turn at 13, did a task at C, travelled by the route CD to D and then went on to E. Altogether, they took one hour for this journey. Find out the actual distance traversed by them and the displacement from A to E. From this, deduce their speed. What was their velocity from A to E in the direction AE’? Can this velocity be called average velocity?
Answer:

Yes, this velocity can be called as average velocity.
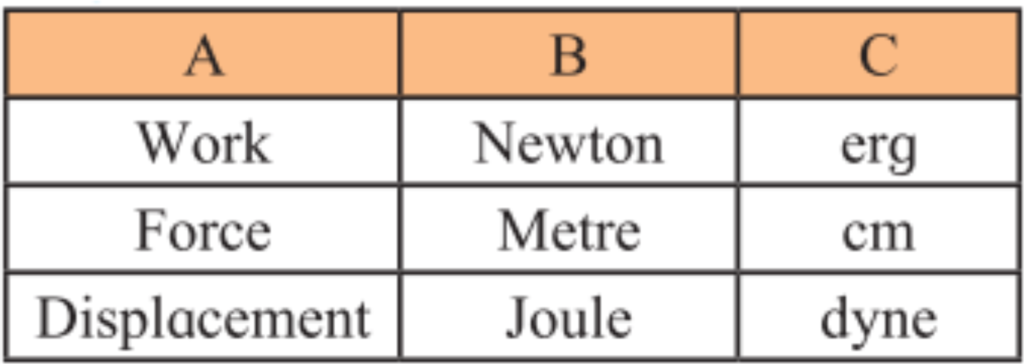
3. From the groups B and C, choose the proper words, for each of the words in group A.
Answer:
| A | B | C |
| Work | Joule | erg |
| Force | Newton | dyne |
| Displacement | Metre | cm |
4. A bird sitting on a wire, flies, circles around and comes back to its perch. Explain the total distance it traversed during its flight and its eventual displacement.
Answer:
The total distance the bird has traversed is the length of the distance covered by circling, but the eventual displacement are the bird is zero as its initial and final position are one and the same.
5. Explain the following concepts in your own words with everyday examples: force, work, displacement, velocity, acceleration, distance.
Answer:
1. Force: The interaction that brings about the acceleration is called force.
e.g: An ox is pulling a cart, applying brakes to a bicycle, lifting heavy iron object with a crane.
2. Work: When an object is displaced by applying a force on it, work is said to be done.
e.g: A bucketful of water is to be drawn from a well and taken to the home by walking from well to home.
3. Displacement: The minimum distance
traversed by a moving body in one direction from the original point to reach the final point is called displacement.
e.g: A rolling of a ball from point A to point B in the same direction.
4. Velocity: Velocity is the distance traversed by a body in a specific direction in unit time.
e.g: A truck is covering a distance of 40km from A to D in a straight line in 1 hour.
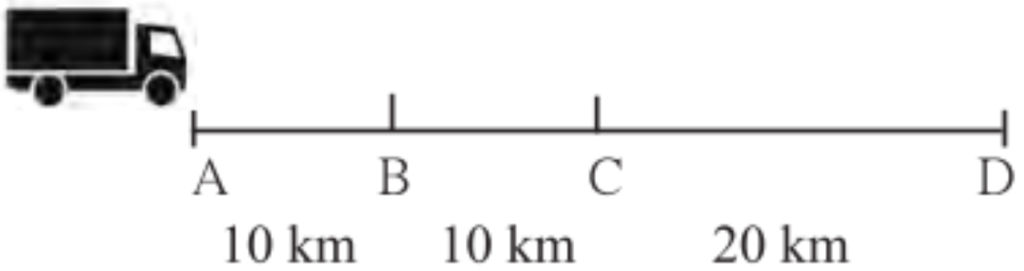
5. Acceleration: It is change in velocity per second. It can be deduced.

(i) In the above example a truck covered the distance AB at velocity of 60 km/hr, BC at 30 km/hr and CD at 40 km/hr.
(ii) It means that the velocity for the distance CD is greater than the velocity for the distance BC.
(iii) From the number of seconds required for this change in velocity to take place, the change in velocity per second can be deduced. This is called acceleration
(iv) Distance: The length of the route actually traversed by a moving body irrespective of the direction is called distance.
e.g: Ranjit travelled 1km. from his home to school.
6. A ball is rolling from A to D on a flat and smooth surface. Its speed is 2 cm/s. On reaching B, it was pushed continuously up to C. On reaching D from C, its speed had become 4 cm/s. It took 2 seconds for it to go from B to C. What is the acceleration of the ball as it goes from B to C.
Answer:
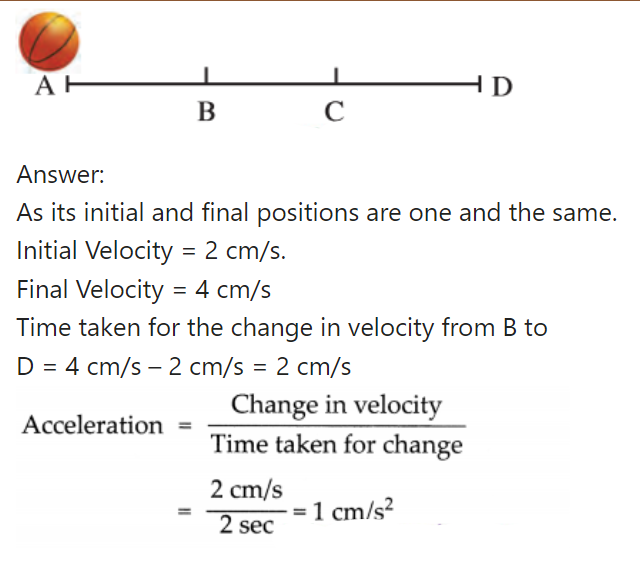
7. Solve the following problems.
a. A force of 1000 N was applied to stop a car that was moving with a constant velocity. The car stopped after moving through 10m. How much is the work done?
Answer:
Force (F) = 1000 N
displacement (s) = 10m
work done (W) = ?
W = Fs
= 1000 × 10
W = 10,000 Joule
b. A cart with mass 20 kg went 50 m in a straight line on a plain and smooth road when a force of 2 N was applied to it. How much work was done by the force?
Answer:
Force (F) = 2 N
Displacement (s) = 50 m
Work done (W) = ?
W = Fs
= 2 × 50
W = 100 Joule


