
1. Fill in the blank with appropriate word:
a. The region in a sound wave, with higher pressure and density is called ………….. and that with low pressure and density is called ……….. .
Answer:
The region in a sound wave, with higher pressure and density is called compression and that with low pressure and density is called rarefaction.
b. Medium is …………… for generation of sound.
Answer:
Medium is needed (or necessary) for generation of sound.
c. The total number of compressions and rarefactions produced per second in a sound wave is 1000. The frequency of the sound wave is ………… .
Answer:
The total number of compressions and rarefactions produced per second in a sound wave is 1000. The frequency of the sound wave is 500 Hz.
[Note: Total number: 100. ∴ 500 compressions and 500 rarefactions are produced per second.]
d. Different sound notes have different ………………. .
Answer:
Different sound notes have different frequencies.
e. In a loudspeaker, …………… energy is converted into ………….. energy.
Answer:
In a loudspeaker, mechanical energy is converted into sound energy.
2. Give scientific reasons:
a. It is essential to change the tension in the vocal cords, as we produce different sound notes from our larynx.
Answer:
Different sound notes correspond to different frequencies. The frequency of sound depends on the tension in the vocal cords. Hence, it is essential to change the tension in the vocal cords, as we produce different sound notes our larynx.
b. Astronauts on the moon cannot hear each other directly.
Answer:
Two astronauts on the moon talking to each other directly, will be unable to listen to each other, even if they are very close to each other. The moon does not have atmosphere. Since there is no medium which is necessary for generation and propagation of sound, between the astronauts, direct sound propagation between them is not possible. Therefore, the astronauts use some technology like the one used in our cell-phones to communicate with each other. The waves used in cell-phone do not need any medium for propagation.
c. As the sound wave propagates from one place to the other in air, the air itself is not required to move from one place to the other.
Answer:
Propagation of sound through air occurs due to energy transfer by vibrating air molecules in one region to those in the adjacent region away from the source. The molecules simply vibrate about their mean positions. Hence, the air itself is not required to move from one place to the other.
3. How are different sound notes generated in musical instruments like guitar, which uses strings for sound generation, and flute, which uses blown air for sound generation?
Answer:
1. Guitar: It is a string based, flat- backed instrument. It has usually six strings, the strings are plucked or strummed with the fingers or a small piece of plastic, wood, etc. It has a flat sounding board with a circular sound hole in the centre. Also it has a fretted fingerboard. Its frequency range is more than three octaves. The frequency of vibration of the string is changed by changing the tension in the string or changing the vibrating length of the string. As the tension is increased, the frequency increases. As the vibrating length is increased, the frequency decreases. This is how different sound notes are generated.
[Note: The acoustic guitar has hollow body and six or twelve strings while the electric guitar usually has solid body and six strings. The electric bass guitar has four strings.]
2. Flute: It is a wind instrument where air is blown against the edge or rim of the blowing hole. The frequency of the sound produced depends upon the length of the vibrating air column in the tube. The greater the length of the vibrating air column, the less is the frequency of the sound produced. This is how different sound notes are produced. The flute has six or seven or eight holes to generate sounds of different frequencies. Different notes can be generated also by changing the way of air-blowing.

4. How is sound produced in the human larynx and a loudspeaker?
Answer:
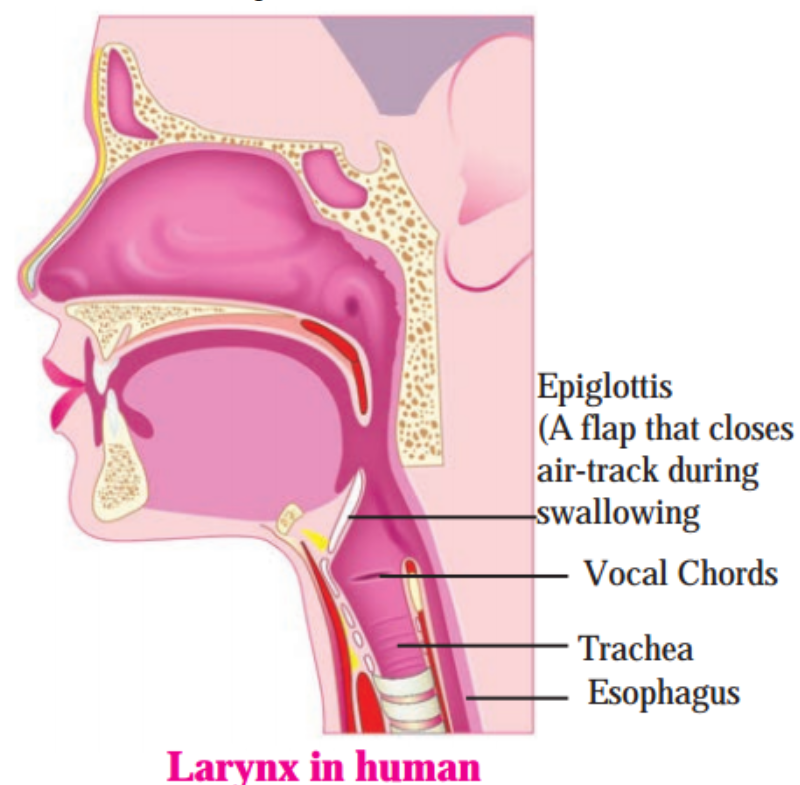
1. Sound production in the human larynx:
In the humans, sound is produced in the voice box called the larynx. It is located at the upper end of the windpipe. Two vocal cords (chords) are stretched across it with a narrow slit between them for the passage of air (Fig. 15.5). When the lungs force air through the slit, the cords start vibrating.
The frequency of the sound produced depends upon the length and thickness of the cords, and the tension in the chords. The frequency increases with the increase in tension and the more the length or the thickness of the cord, the less is the frequency. Muscles attached to the cords can make the cords tight (more tension) or loose (less tension).
2. Sound produced in a loudspeaker:
Figure shows the internal construction of a loudspeaker. Here, a coil is wound around a permanent magnet. The conical screen of the loudspeaker is attached to the coil.
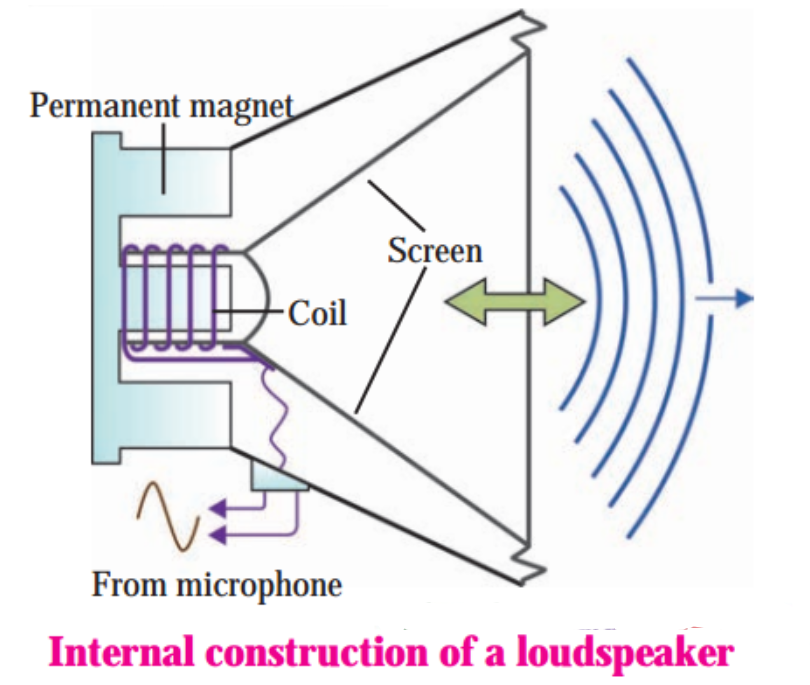
When a current is passed through the coil, a magnetic field is produced. Its interaction with the permanent magnet results in the back and forth motion of the coil. The frequency and the amplitude of the motion of the coil depends on the variation in the current through the coil.
As the coil moves, the conical screen also moves back and forth. The vibrations of the screen produce sound waves in air. Very loud sound can be produced by changing the current.
[Note: If you gently touch the vibrating screen, you can feel the vibrations.]
5. Explain the experiment, with a neat diagram, to prove the following:
‘Sound needs a material medium for propagation.’
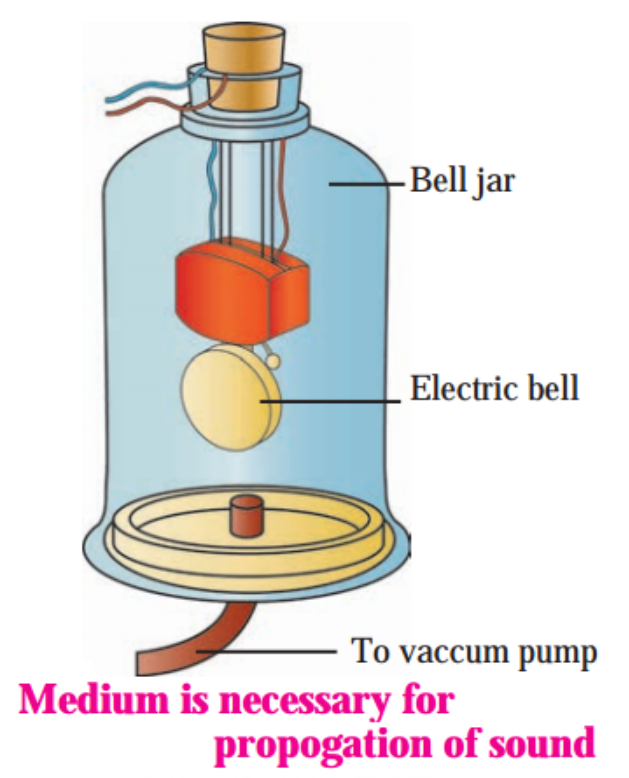
Answer:
Figure shows part of the set up used in this experiment. What is not shown is the electric circuit in which the electric bell is connected. A vacuum tight bell jar contains an electric bell connected to a power supply through the lid of the jar. The jar is placed on a smooth horizontal surface such as that of glass.
Initially the vacuum pump is off and the jar contains air. The circuit containing the bell is completed using the key or the switch so that the bell starts ringing. This can be heard outside the jar.
Then the vacuum pump is switched on so that it starts removing the air from the jar. We find that the level of ringing sound heard goes on decreasing as the quantity of air in the jar becomes less and less.
When the pump is operated for a sufficiently long time interval, the quantity of air in the jar becomes so less that the level of ringing sound becomes very low; sound is hardly audible. But we can see the striker in the bell hitting the gong. By extrapolation, we conclude that sound generation and propagation needs a medium.
6. Match the following:
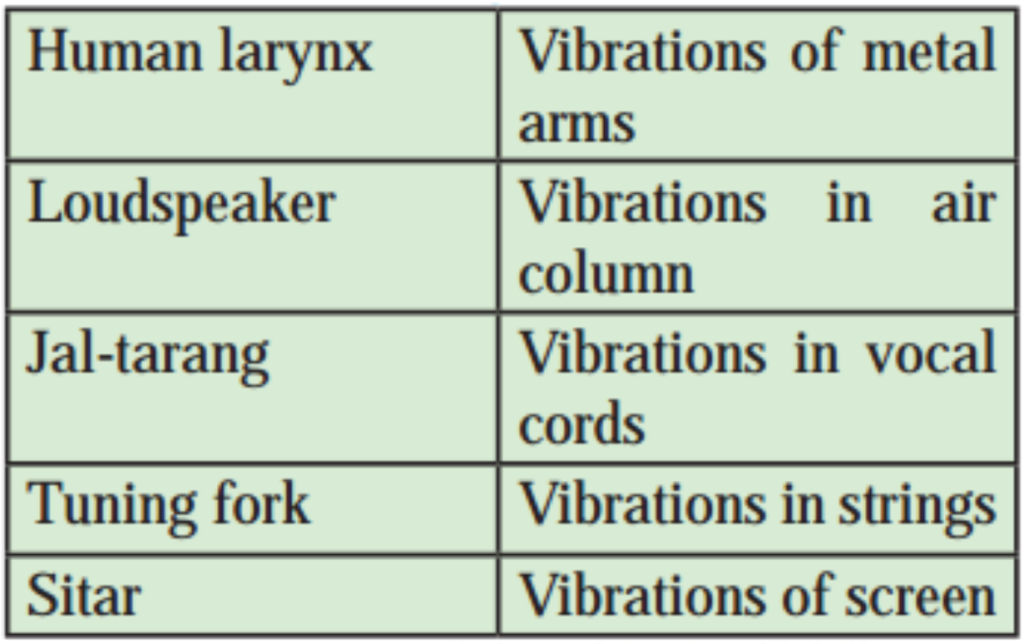
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| Human larynx | Vibrations in vocal cords |
| Loudspeaker | Vibrations of screen |
| Jaltarang | Vibrations in air column |
| Tuning fork | Vibrations of metal arms |
| Sitar | Vibrations in strings |


