1. Give examples of 3 plants that have:
(a) Spiny fruits
Answer:
Jack fruit, Pineapple, Lychee (litchi), Datura
(b) Spiny stem
Answer:
Cactus, Wild rose, Catclaw acacia, Silk, Cotton
(c) Red flowers
Answer:
Rose, Dahlia, Hibiscus, Tulips,
(d) Yellow flowers
Answer:
Marigold, Daffodil, Sunflower, Daisy
(e) Leaves that close at night
Answer:
Mimosa plant, Tallwood, Prayer plant, Gulmohar
(f) Single seeded fruits
Answer:
Mango, Lychee, Jamun
(g) Many seeded fruits
Answer:
Custard apple, Papaya, Watermelon.
2. Observe any one flower and its various parts and describe it in your own words.
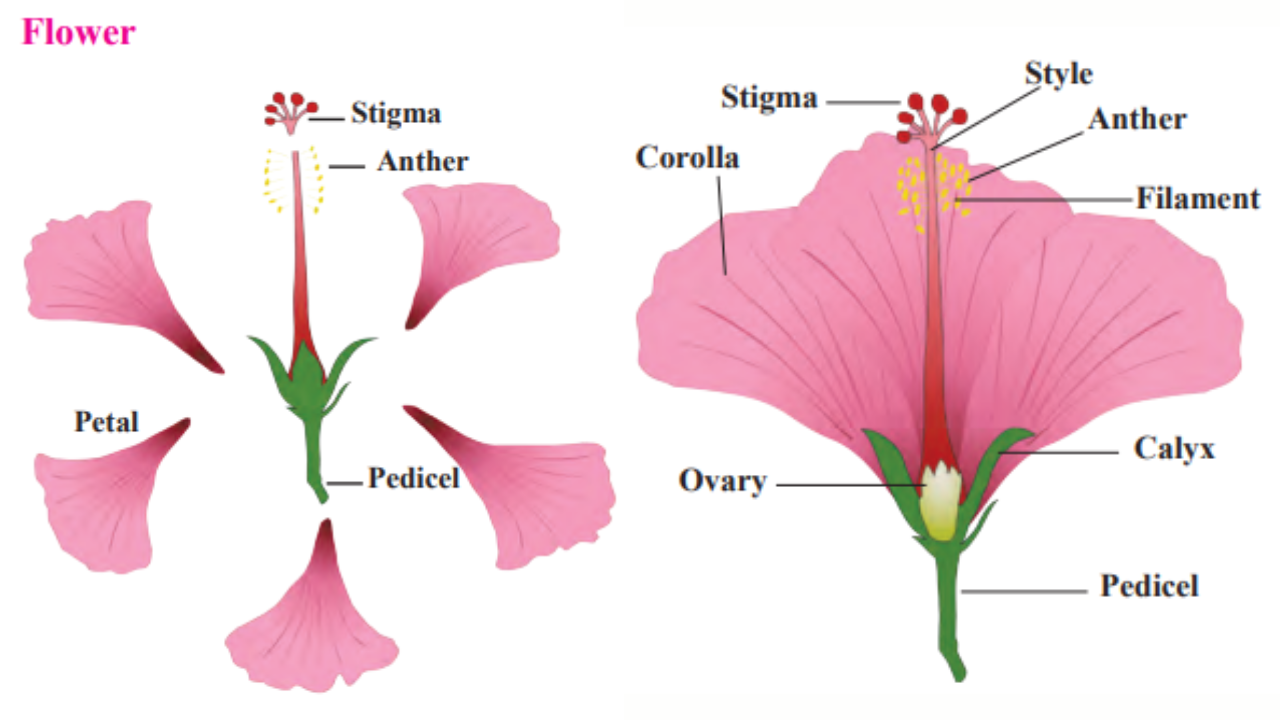
A flower has the following parts:
1. Pedicel:
(a) The flower may have a long or a short stalk called a pedicel.
(b) One end of the pedicel is attached to the stem,
(c) The other end of the pedicel is expanded and swollen. It is called the receptacle, (d) Petals and other flower parts are supported on the receptacle.
2. Calyx: In the bud condition, the petals are covered by leaf-like parts called green sepals. They form the calyx.
3. Corolla: This is made up of colourful parts called petals.
4. Androecium:
(a) This is the male reproductive part of the flower.
(b) It consists of stamens.
(c) Each stamen is made up of anther and filament.
5. Gynoecium:
(a) This is the female reproductive part of the flower.
(b) This is made up of carpels.
(c) A carpel consists of a stigma, style and ovary.
3. What are the similarities and differences between them?
(a) Jowar and Moong
Differences:
| Jowar | Moong |
| i. It has fibrous roots. | i. It has tap root. |
| ii. It is a monocotyledonous seed. | ii. It is a dicotyledonous seed. |
| iii. It is a rabi crop. | iii. It is a Kharif crop |
(b) Onion and Coriander
Differences:
| Onion | Coriander |
| i. It is a type of monocot plant | i. It is a type of dicot plant. |
| ii. It is a type of vegetable | ii. It is a type of herb |
| iii. The edible part is a bulb | iii. The edible part is leaf and stem |
- Both are used in cooking.
- Both are edible.
- Both belong to kingdom plantae.
(c) Leaves of banana and Leaves of mango
Answer:
| Leaves of banana | Leaves of mango |
| i. It has parallel venation. | i. It has reticulate venation. |
| ii. It is very large in size. | ii. It is small in size. |
| iii. It is a monocotyledonous plant. | iii. It is a dicotyledonous plant. |
Similarity: Both the plants are perennial.
(d) Coconut tree and Jowar stalk plant
Answer:
| Coconut tree | Jowar stalk plant |
| i. It is tall and has a thick stem | i. It is small and has a thin stem. |
| ii. It has strong root system. | ii. It has weak root system. |
| iii. Every part of the tree is useful. | iii. Only seeds are useful. |
Similarities:
- Both are from the same kingdom Plantae.
- Both are autotrophic.
- Both are monocotyledonous plants.
4. Explain the following images in your own words.
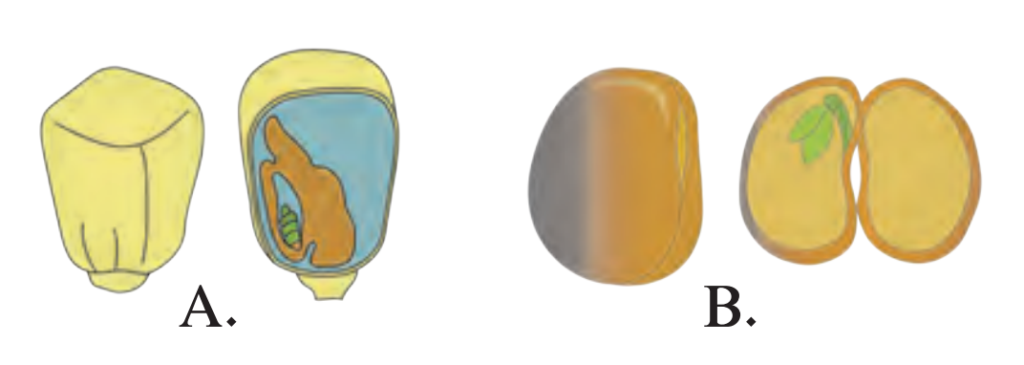
Answer:
- Diagram A is of maize seed. It is a monocotyledonous seed and does not divide into two equal parts. The plant has a fibrous root system.
- Diagram B is of bean seed. It is a dicotyledonous seed and it divides into two equal parts. The plant has a tap root system.
5. Describe the functions of various parts of a plant.
Answer:
The functions of various parts of a plant are as below.
1. Root: (a) Fixation: It anchors the plant body to the soil, so helps in fixation, (b) Absorption: It absorbs water and nutrients from the soil, so helps in absorption, (c) Conduction: The root translocates water and mineral salts into the stem. (d) Storage: A certain amount of food is stored in the root which is utilized as it grows.
(e) Preventing soil erosion: It helps to bind the soil particles and prevent them from being blown away by wind or water.
2. Stem: (a) It supports and holds leaves, flowers and fruits, (b) The stem conducts the water and minerals from roots to leaves and fruits, (c) It stores the food.
3. Leaves: (a) It synthesizes food for the plant, (b) Stomata, the tiny openings in the leaf help in gaseous exchange and are responsible for the process of transpiration.
4. Flower: It helps in pollination.
5. Fruit: (a) It protects the seed, (b) It helps in seed dispersal.
6. Seed: A new plant develops from it.
6. Certain properties are mentioned below. Find a leaf corresponding to each property and describe those plants.
leaves with smooth surface, leaves with rough surface, fleshy leaf, spines on leaf.
Answer:
- Leaves with smooth surface: e.g. Banana leaf. It is large in size. It is closely rolled up one over the other. Together they look like a trunk but they form only an apparent trunk. It has parallel venation.
- Leaves with rough surface: e.g. Hibiscus leaf. It has reticulate venation. Leaf margin is toothed.
- Fleshy leaf: e.g. Jade plant, water hyacinth. It has fleshy, glossy and smooth leaves. They are coloured jade green and having a slightly red tinge towards the edge of leaves when exposed to higher level of light.
- Spines on leaf: e.g. Opuntia, Ci/cas, kevda. Opuntia is a desert plant. Leaf is thick, fleshy and having spines on it.
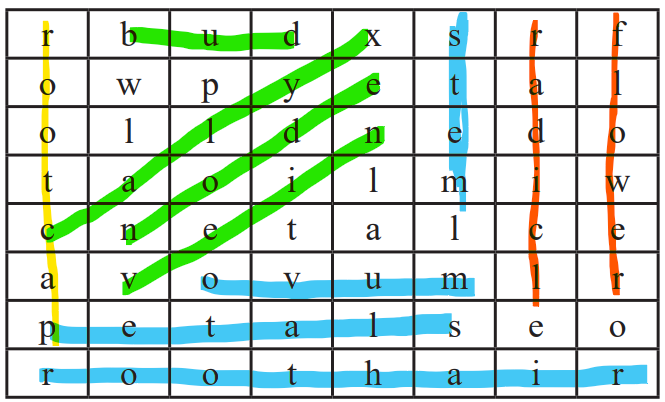
7. Find the plant parts.
Answer
ROOT, ROOT CAP, ROOT HAIR, BUD, PETALS, STEM, RADICLE, FLOWER, LEAF, VEIN, CALYX, NODE, OVUM.