
1. Answer the following.
a. What is the difference in the atomic models of Thomson and Rutherford?
Answer:
| Thomson’s atomic model | Rutherford’s atomic model |
| 1. According to Thomson’s atomic model, the negatively charged electrons are embedded in a gel of positive charge. | 1. According to Rutherford’s atomic model the negatively charged electrons revolve around the nucleus. |
| 2. Atom is homogenous sphere of positive charge. | 2. The positive charge is in the nucleus of the atom. |
b. What is meant by valency of an element? What is the relationship between the number of valence electron and valency?
Answer:
Valency: The capacity of an ; element to combine with another element is known as valency.
Valence electrons: The electrons in the outermost shell of an atom of an element are called valence electrons.
Helium and neon, atoms of both these gaseous element do not combine with any other atom. These elements are chemically inert, i.e. their valency is zero.
Helium atom contains two electrons, indicates that the outermost shell of helium has an electron duplet. The valence shell of neon is completely filled, i.e. neon has an electron octet. Similarly argon contains eight electrons in the valence shell, i.e. argon has an electron octet. It is confirmed that the valency is zero when electron octet (or duplet) is complete.
Atoms of all the elements except inert gases have tendency to combine with other atoms, i.e. they have a non zero valency. The molecules formed by combination with hydrogen (E.g. H2, HCl) that valency of hydrogen is one. The electronic configuration of hydrogen shows that there is one electron less than the complete duplet state. This number ‘one’ matches with the valency of hydrogen which is also one.
It means that there is relationship between the valency of an element and the number of electrons in its valence shell.
c. What is meant by atomic mass i number? Explain how the atomic number and mass number of carbon are 6 and 12 respectively.
Answer:
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom is called the atomic mass number. The atomic number, i.e. the proton number of carbon is 6 and the mass number is total number of protons and neutrons in the carbon, i.e. 6 protons + 6 neutrons = 12. Therefore, the atomic number and mass number of carbon are 6 and 12 respectively.
d. What is meant by subatomic particle? Give brief information of three subatomic particles with reference to electrical charge, mass and location.
Answer:
A particle which is a constituent of an atom hence smaller than the atom is called subatomic particle.
An atom is formed from the nucleus and the extranuclear part. These contain three types of subatomic particles.
The nucleus contains two types of subatomic particles together called nucleons. Protons and neutrons are the two types of nucleons or subatomic particles and electrons are subatomic particles in the extra nuclear part.
1. Proton (p): Proton is a positively charged subatomic particle in the atomic nucleus. The positive charge on the nucleus is due to the proton in it. A proton is represented by the symbol ‘p’. Each proton carries a positive charge of +1e. (1e = 1.6 × 10-19 coulomb). When total positive charge on the nucleus is expressed in the unit ‘e’, its magnitude is equal to the number of proton in the nucleus.
The mass of one proton is approximately lu (1 Dalton).
(1u = 1.66 × 10-27g) (The mass of one hydrogen atom is also approximately lu.)
2. Neutron (n): Neutron is an electrically neutral subatomic particle and is denoted by the symbol ‘n’. The number of neutron in the nucleus is denoted by the symbol ‘N’ Atomic nuclei of all the elements except hydrogen with atomic mass lu, contain neutrons. The mass of a neutron is approximately lu, which is almost equal to that of a proton.
3. Electron (e–): Electron is a negatively charged subatomic particle and is denoted by the symbol ‘e-’. Each electron carries one unit of negative charge (-1e). Mass of an electron is 1800 times less than that of a hydrogen atom. Therefore the mass of an electron can be treated as negligible. Electron in the extranuclear part revolve in the discrete orbits around the nucleus. The energy of an electron is determined by the shell in which it is present.
2. Give scientific reasons:
a. All the mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus.
Answer:
- The nucleus of an atom contains protons and neutrons.
- The electrons revolve around the nucleus.
- The mass of an electron is negligible compared to that of a proton or a neutron.
- Hence, the mass of an atom depends mainly on the number of protons and neutrons. Therefore, practically all the mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus.
b. Atom is electrically neutral.
Answer:
- An atom is made of two parts, viz. the nucleus and the extranuclear part.
- The nucleus is positively charged. The positive charge on the nucleus is due to protons.
- The extranuclear part of an atom is made of negatively charged electrons.
- In an atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of extranuclear electrons.
- The magnitude of the positive charge on the nucleus equals the magnitude of the negative charge on the electrons. As the opposite charges are balanced, the atom is electrically neutral.
c. Atomic mass number is a whole number.
Answer:
- The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom is called the atomic mass number (A).
- As protons and neutrons are whole numbers, the atomic mass number is also a whole number.
d. Atoms are stable though negatively charged electron are revolving within it.
Answer:
- The entire mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus and the positively charged nucleus at centre of an atom.
- The negatively charged electrons revolve around the nucleus.
- The total negative charge on all the electron is equal to positive charge on the nucleus. As the opposite charges are balanced, the atom is stable.

3. Define the following terms.
a. Atom:
Answer:
An atom is the smallest particle of an element which retains its chemical identity in all physical and chemical changes.
b. Isotope
Answer:
Atoms of the same element having the same atomic number, but different atomic mass numbers are called isotopes.
c. Atomic number
Answer:
The number of electrons or protons in an atom is called the atomic number. It is denoted by Z.
d. Atomic mass number
Answer:
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom is called the atomic mass number. It is denoted by A.
e. Moderator in nuclear reactor
Answer:
The substance which reduces the speed of fast-moving neutrons produced in a fission is called a moderator.
4. Draw a neal labelled diagram.
a. Explain Rutherford’s scattering experiment.
Answer:
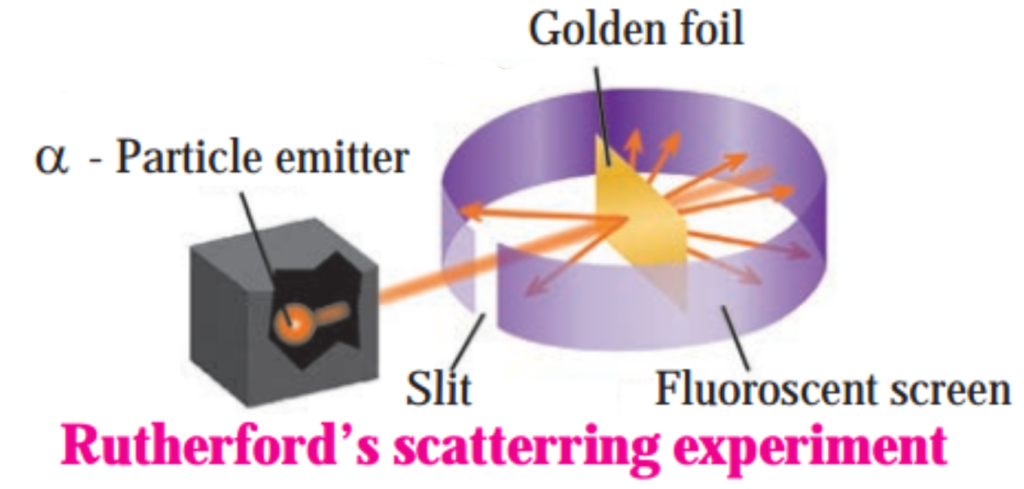
Alpha particles emitted by radioactive element bear a positive charge. Rutherford bombarded alpha particles through a very thin gold foil. He observed the path of α – particles by means of a fluorescent screen around the gold foil. It was expected that
- Most of the alpha particles passed through the gold foil without any deviation.
- Some alpha particles were deflected from their path through small angles.
- A few alpha particles were scattered at large angles.
- A still smaller number of same sign particles get deflected through a larger angle and one a-particle out of 20000 bounced back in the direction opposite to the original path.
b. Thomson’s atomic model.
Answer:
Thomson’s plum pudding model of atom:
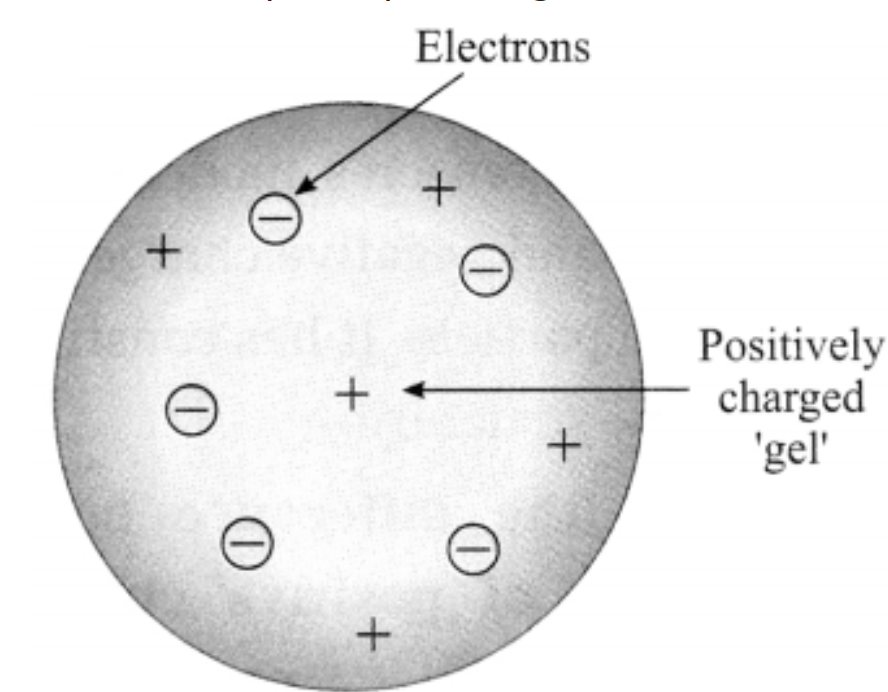
- According to Thomson’s model the positive charge is distributed throughout the atom and the negatively charged electron: are embedded in a gel of positive charge (a plum pudding model).
- The distributed positive charge is balanced by the negative charge on the electrons. Therefore the atom becomes electrically neutral.
c. Diagrammatic sketch of electronic configuration of magnesium (Atomic number 12).
Answer:

d.
Diagrammatic sketch of electronic configuration of argon (Atomic number 18).
Answer:

5. Fill in the blanks.
1. Electron, proton, neutron are the types of ………… in an atom.
Answer:
Electron, proton, neutron are the types of subatomic particles in an atom.
2. An electron carries a ……………. charge.
Answer:
An electron carries a negative charge.
3. The electron shell ………….. is nearest to the nucleus.
Answer:
The electron shell K is nearest to the nucleus.
4. The electronic configuration of magnesium is 2, 8, 2. From this it is understood that the valence shell of Magnesium is …………….. .
Answer:
The electronic configuration of magnesium is 2, 8, 2. From this it is understood that the valence shell of Magnesium is M.
5. The valency of hydrogen is one as per the molecular formula H2O. Therefore valency of ‘Fe’ turns out to be ………….. as per the formula Fe2O3.
Answer:
The valency of hydrogen is ‘one’ as per the molecular formula H2O. Therefore valency of ‘Fe’ turns out to be 3 as per the formula Fe2O3.
6. Match the pairs.
Question 1.
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Proton | a. Negatively charged |
| 2. Electron | b. Neutral |
| 3. Neutron | c. Positively charged |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Proton | c. Positively charged |
| 2. Electron | a. Negatively charged |
| 3. Neutron | b. Neutral |
7. Deduce from the datum provided.
Question 1.
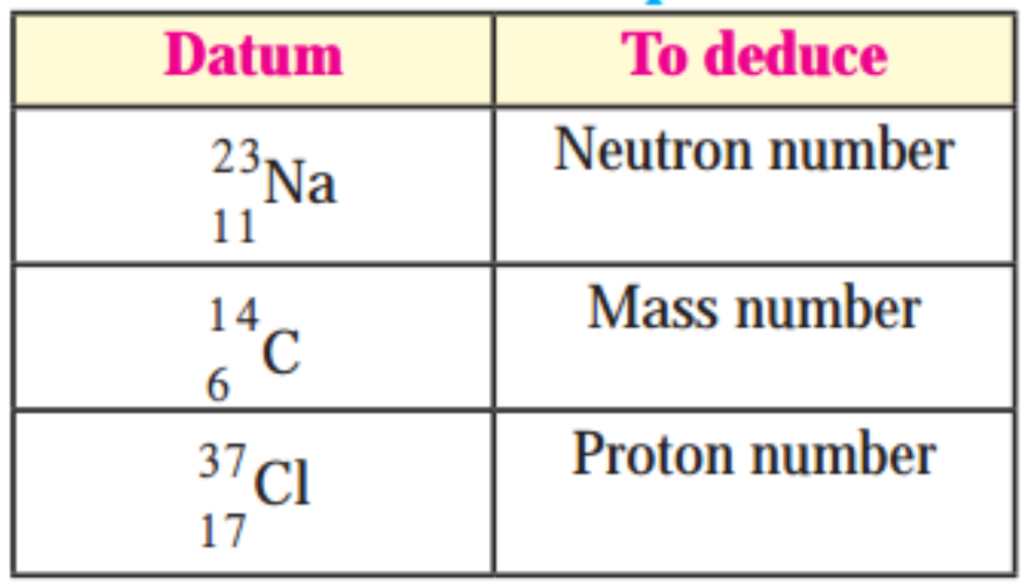
Answer:
1. There are 12 neutrons in the sodium (2311Na).
(N = A – Z) 23 – 11 = 12
2. Atomic mass number of 146C is 14.
3. There are 17 protons in chlorine (1737Cl)


