1. Write the proper words in the blanks:
(meridian, horizon, twelve, nine, apparent, celestial, ecliptic)
a. When seen from a great distance, the sky seems to be touching the ground along a circle. This circle is called the …………… .
Answer:
horizon
b. The ………….. is used while defining the zodiac sign.
Answer:
meridian
c. Classified according to seasons, one season will have ………… nakshatras.
Answer:
nine
d. The rising of the sun in the east and its setting in the west is the ………. motion of the sun.
Answer:
apparent
2. A star rises at 8 pm. tonight. At what time will it rise after a month? Why?
Answer:
- Stars rise and set 4 minutes earlier every day. If star rises at 8 pm tonight, it will rise at 7:56 pm tomorrow.
- It will rise at 5:24 pm after a month.
- The sun and the moon are seen to move from the west to the east against the background of stars.
- The sun moves through one degree every day and the moon through 12 to 13 degrees.
- This happens due to the motion of the earth around the sun and the moon around the earth which affects the duration of the stars and shortens its time period.
3. What is meant by “The sun enters a nakshatra?” It is said that in the rainy season the sun enters the mrug nakshatra. What does it mean?
Answer:
- When we look at the sun we see not only the sun but also constellation behind the sun.
- The constellation cannot be seen in bright sunlight but it is indeed present behind the sun.
- As the earth changes its position, a different constellation or zodiac sign or raashi appears behind the sun.
- This is what we express when we say that the sun enters a particular zodiac sign or raashi.
- In rainy season due to the perceived motion of the sun, it enters mrug nakshatra and that is how it is expressed.
4. Answer the following questions.
a. What is a constellation?
Answer:
A group of stars occupying a small portion of the celestial sphere is called a constellation.
b. What points should be considered before a skywatch?
Answer:
- The place for sky watching should be away from the city and as far as possible it should be new moon night.
- Binoculars or telescopes should be used for skywatch.
- Identifying the pole star in the north makes the skywatch easier. Hence the pole star should be used as a reference point for skywatch.
- As the stars in the west set early, sky watching should begin with stars in the west.
- (a) On a sky map, the north and south are towards the bottom and top of the map respectively, (b) This is because the sky map is to be held overhead in such a way that the direction we face is at the bottom side.
c. It is wrong to say that the planets, stars and nakshatras affect human life. Why?
Answer:
- Science has proved that the constituents of the solar system e.g. planets, satellites and comets as also distant stars and constellations do not have any influence on human life.
- Man has stepped on the moon and will conquer Mars in the 21st century.
- Hence, in this age of science, holding on to beliefs which have been proved wrong by numerous scientific tests, is an unnecessary waste of time and energy.
- It is important to consider all these issues with a scientific frame of mind.
5. Write a paragraph on the birth and life cycle of stars using following figure.
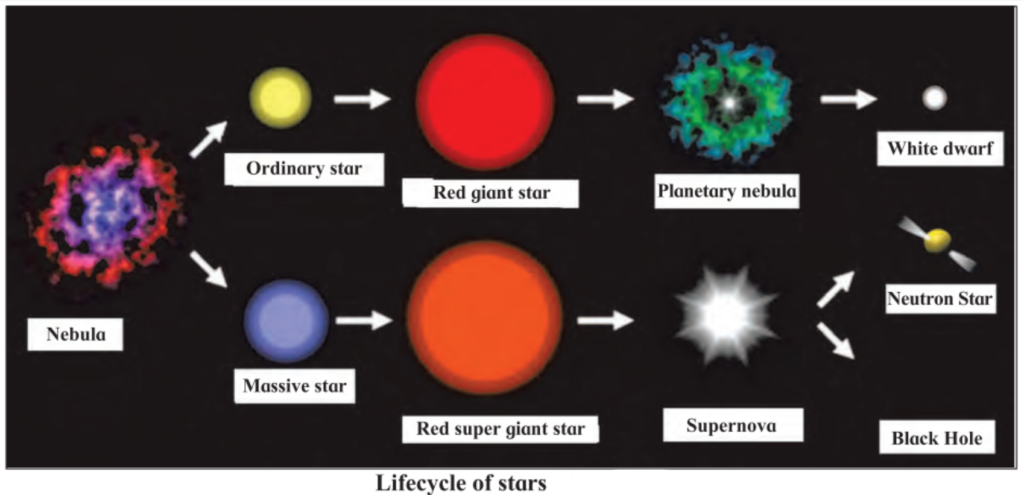
Answer:
Stars are born out of nebulae. Nebulae are clouds made up mainly of hydrogen gas and dust particles which are attracted towards one another by the force of gravity, (i) As a result of pressure, the internal temperature increases and the cloud becomes dense and spherical in shape, (ii) From the diagram, life cycle of two stars can be explained.
(a) Ordinary star:
(i) The ordinary star forms a Red giant star at the later stage of its evolution when it runs out of hydrogen gas at its core.
(ii) At the end stage of its life it forms a white dwarf. Stars like the sun become white dwarf when its nuclear fuel is totally exhausted.
(iii) It is 1% in diameter of its original size.
(b) Massive Star:
(i) Massive star forms Red super giant star at the end of its life cycle,
(ii) They are also called super red giants with a relatively cool outer surface,
(iii) Supernova is the explosive death of the star of the end of its life with the brightness of 100 million stars in a short amount of time,
(iv) A neutron star is the dense core of the supernova.
(v) It is the smallest and the densest star known to exist with a 10 km radius,
(vi) Neutron stars sometimes end as a black hole,
(vii) Black holes are not seen from telescopes and are identified by their intense gravitational pull where even light cannot escape.


